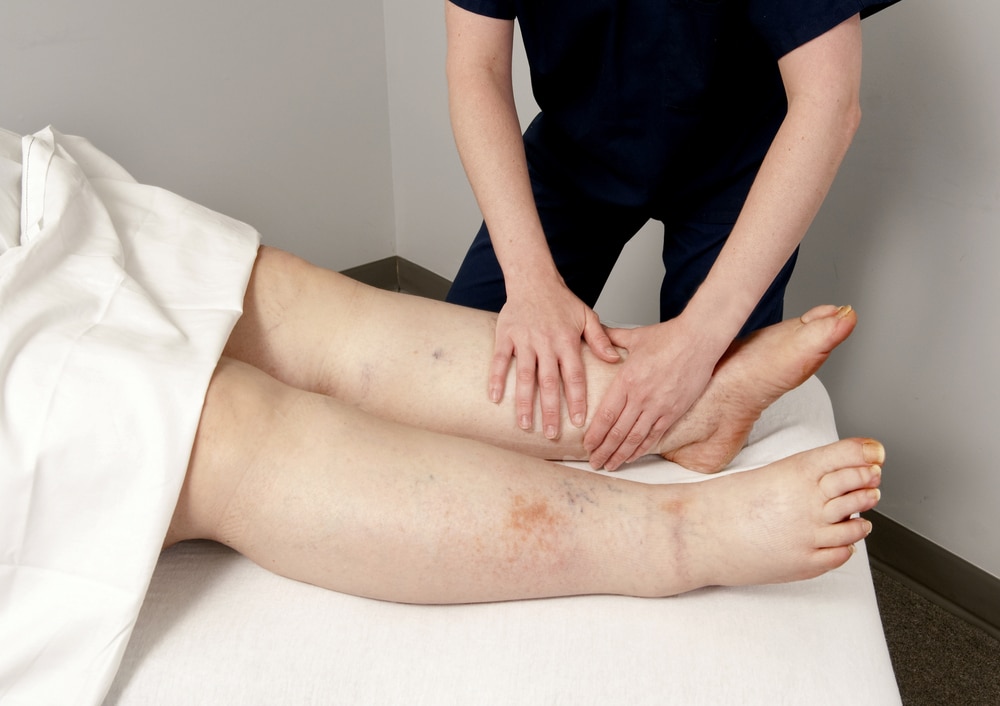
Lymphedema is a chronic condition characterized by the swelling of limbs due to a build-up of lymphatic fluid, often causing discomfort and limited mobility. While there is currently no cure for this condition, effective treatments are available that can manage symptoms and improve your quality of life.
At Venus Vein Clinic in Omaha, NE, we specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of venous and lymphatic diseases. With Dr. Schroeder at the helm, a board-certified vein and lymphatic specialist with the most experience in the Omaha metro area, we offer various treatment options designed to provide symptom relief and enhance your daily activities.
What Is Chronic Swelling?
In the regular course of blood flow, fluid naturally seeps into nearby tissues from your vascular network. This fluid is then collected by your body’s lymphatic system. When there is an unusual accumulation of this fluid, it results in a condition known as edema, or swelling. While short-term mild swelling can have a variety of causes, persistent edema is often indicative of a more serious underlying health issue. Conditions that could lead to chronic edema encompass congestive heart failure, renal and hepatic diseases, chronic venous insufficiency, and lymphedema.
What Is Lymphedema?
Lymphedema is a long-term, advancing disorder characterized by the buildup of protein-rich fluids in the interstitial spaces, or the areas between cells. This condition arises due to the malfunctioning of the lymphatic system, which is normally responsible for removing these fluids and proteins and returning them to the blood circulation. A dysfunctional lymphatic system exposes the individual to potential health risks, such as repeated skin infections, commonly referred to as cellulitis.
What Are the Causes of Lymphedema?
The causes of lymphedema can depend on the type of the condition that you have:
Primary Lymphedema
This form of lymphedema is usually inherited and may manifest shortly after birth, during puberty, or in adulthood. It arises from a developmental issue with the lymphatic system.
Secondary Lymphedema
More commonly occurring, secondary lymphedema develops as a result of damage to the lymphatic system or from its blockage. This is often due to:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of lymph nodes can disrupt normal lymphatic flow, leading to lymphedema.
- Radiation Therapy: Exposure to radiation can damage or scar the lymphatic channels, causing fluid accumulation.
- Infection: Certain bacterial or parasitic infections can impair the lymphatic system, contributing to the onset of lymphedema.
- Injury or Trauma: Physical damage to the lymphatic system can also be a contributing factor.
- Cancer: Tumors can block the lymphatic system either by direct invasion or by exerting pressure on the lymphatic vessels.
Symptoms of Lymphedema
- Unusual swelling (edema)
- Swelling of the dorsum of the foot
- Swollen or squared-off toes
- Heaviness or tightness in the affected limb(s)
- Restricted range of motion
- Lymph fluid discharge from the skin (lymphorrhea)
- Skin Changes
- “Orange peel” skin appearance
- Thick, rigid skin (hyperkeratosis and fibrosis)
- Bumpy wrinkling of the skin (papillomatosis)
- Ulcerations of the skin
Diagnostic Methods for Lymphedema
The diagnostic process for lymphedema typically starts with an in-depth discussion about your symptoms to understand their onset, duration, and severity. Following this, a physical examination is conducted to evaluate the extent of the swelling and to look for other indicative signs such as skin changes or limitations in range of motion.
In some instances, an ultrasound may be recommended to further assess the condition of the lymphatic channels and to rule out other potential issues like blood clots. The advantage of undergoing diagnosis at our office is that tests like ultrasound can be performed on the same day as your appointment, eliminating the need for a follow-up visit for testing. This allows for immediate next steps in creating your treatment plan.
Risk Factors for Lymphedema
While anyone can develop lymphedema, certain factors increase the risk of developing this condition. A history of cancer treatments like radiation therapy or surgical removal of lymph nodes can make you more susceptible. Infections affecting the lymphatic system are another potential risk factor. Physical trauma or injuries that impact the lymphatic channels can also contribute to the development of lymphedema.
Being overweight or obese may put extra strain on an already compromised lymphatic system. Age can also play a role. As you get older, your body’s mechanisms for fluid balance can become less efficient, raising the risk of lymphedema. Knowing these risk factors helps us tailor a more effective treatment plan.
Treatment of Lymphedema
There is currently no cure for lymphedema. However, it is important to treat it since the condition can get worse over time, leading to increased swelling and pain, fibrosis (a hardening of the skin), and infections like cellulitis that can continue to be a problem. Lymphedema can decrease mobility, dexterity, range of motion, and the ability to perform daily activities. It also may significantly increase the cost of healthcare. However, effective management of symptoms is possible. Proper diagnosis of the condition is often critical to achieving effective treatment.
Management of lymphedema is achieved with a combination of therapist-directed in-clinic treatment and at-home self-management with a pneumatic compression device. By seeking out treatments, you can improve your quality of life and help prevent complications from occurring.
What Are the Benefits of Pneumatic Compression Therapy for Lymphedema?
Non-Invasive Lymphedema Therapy
Pneumatic compression as a form of lymphedema therapy is non-invasive. With no need for surgical procedures or injections, it serves as a comfortable option for alleviating symptoms.
Lower-Cost Lymphedema Treatment
Pneumatic compression often comes at a lower cost compared to more invasive treatment options. This cost-effectiveness makes it an accessible lymphedema treatment for a broader range of patients.
Minimizing Infections in Swollen Limbs
The therapy can be highly effective in reducing fluid accumulation, which makes it a preferred option for swollen limb treatment. By effectively managing fluid buildup, the risk of skin infections can be reduced.
Improved Overall Health and Lymphedema Management
One of the long-term benefits of this therapy is its contribution to improved overall health and well-being. Effective lymphedema management through pneumatic compression allows you to experience relief from symptoms, enabling you to engage more in your daily activities.
Lymphedema Treatment Before and After
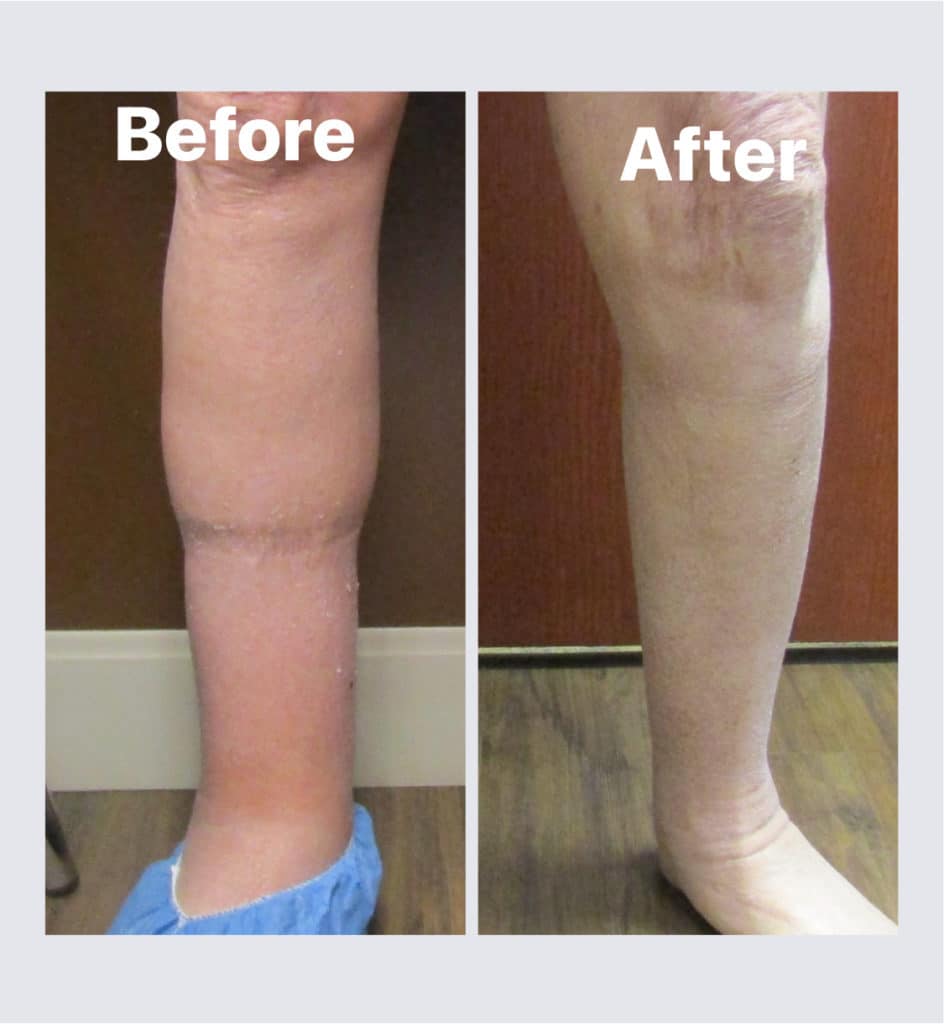
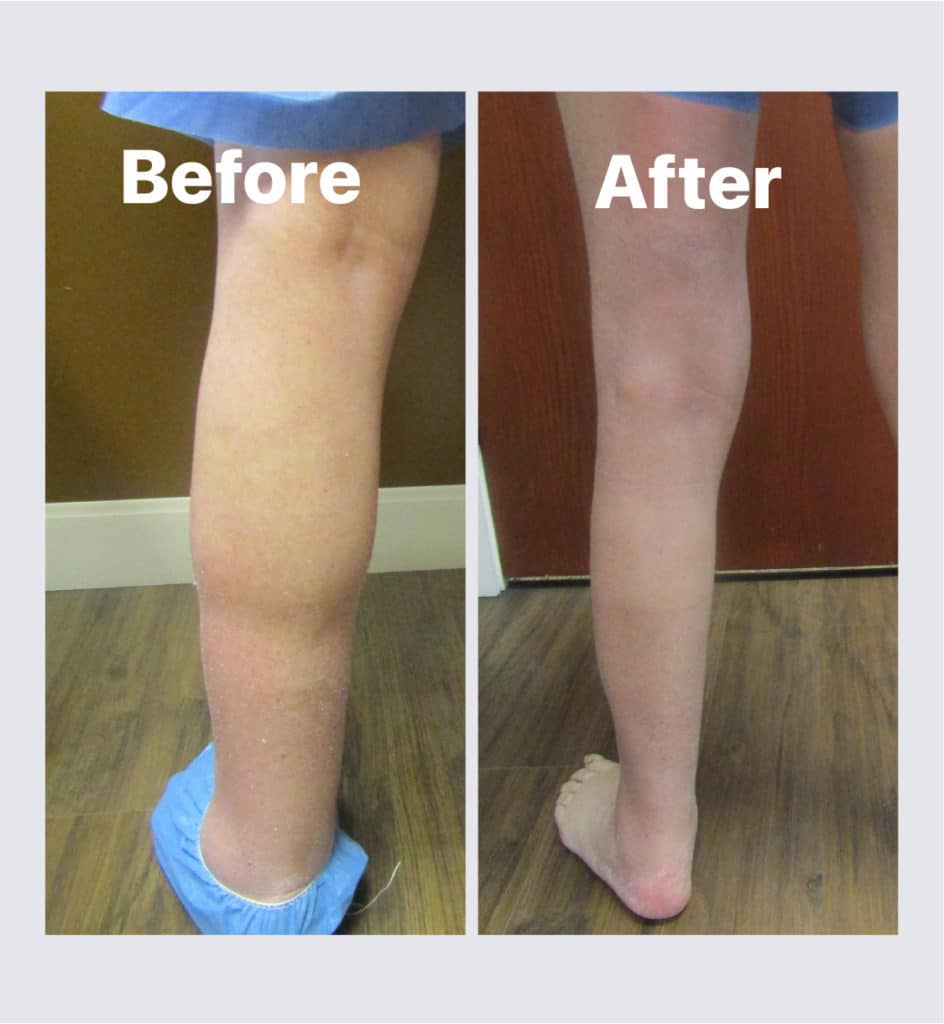
What You Can Expect From Lymphedema Treatment
Evaluation and Diagnosis for Lymphedema
The first step in addressing lymphedema involves a comprehensive evaluation and diagnosis. Through an in-depth discussion about your symptoms, followed by a physical examination and, if necessary, ultrasound tests, we aim to determine the severity of your condition and the underlying causes.
Development of a Treatment Plan
Based on the diagnosis, a personalized treatment plan is formulated to manage your symptoms effectively. This plan is tailored to your unique needs and may include a combination of therapies and lifestyle modifications.
Pneumatic Compression for Lymphedema Management
When it comes to pneumatic compression we start with in-office treatments that can be continued at home. The process involves the use of inflatable garments wrapped around the affected limb. These garments inflate and deflate in a specific pattern to promote lymphatic flow. Many patients describe the sensation as similar to a sequence of gentle squeezes. Elevating your legs during the treatment can further aid in reducing swelling and improving lymphatic drainage.
Follow-Up Appointments At Our Vein Center
Continuous monitoring of your lymphedema is crucial for effective management. Follow-up appointments at our vein center offer the opportunity to reassess your condition, make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan, and ensure that the therapies are providing the expected relief.
Prevention Strategies for Lymphedema
Although lymphedema may not always be fully preventable, certain strategies can minimize the risk or slow its progression. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in moderate exercise can help improve lymphatic circulation, while proper skin care can prevent infections that exacerbate the condition. The use of professionally fitted compression garments and elevating the affected limb can also assist in managing fluid buildup. These strategies can be valuable additions to your ongoing lymphedema treatment for better symptom management.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lymphedema Treatment
How Often Will I Need to Use the Pneumatic Compression Device?
The frequency of using the pneumatic compression device varies depending on individual needs and the severity of your condition. Regular, typically daily, use is generally recommended for effective lymphedema management, but your healthcare provider will offer a personalized schedule that best suits you.
How Long Does Each Session Last?
Usually, it is recommended to use the pump for an hour each day. The duration of each pneumatic compression session can vary, again depending on individual circumstances and treatment goals. Your healthcare provider will give you an idea of what to expect in terms of session length during your lymphedema therapy consultation.
Is the Pneumatic Compression Device Covered By Insurance?
Coverage for pneumatic compression devices varies between insurance plans. Many insurance plans will cover the pneumatic compression device, especially for cases that are medically necessary. It’s essential to consult with your insurance provider to understand the extent of coverage and any out-of-pocket costs you may incur.
Resolving Lymphedema Symptoms With Personalized Treatments
Managing lymphedema effectively requires specialized care and a tailored treatment plan. At Venus Vein Clinic in Omaha, NE, we are committed to offering comprehensive solutions for your condition. To learn more or schedule an appointment, call us today at (402) 979-8346 or fill out our online form.
